
The R group, or side chain, is unique for each amino acid as a result, the a-carbon is a chiral center, except for glycine where R = hydrogen. Also, some amino acids have unique traits that add to their functionality Carbon SkeletonĪll of the amino acids are composed of an amine(-NH 2) and a carboxylicacid (-COOH) linked by a central a-carbon (Figure 2). To learn pH effects or the physicochemical properties of individual AAs, it’s best to try to understand the process and how changing the microenvironment will alter how an AA will behave. Also be keen on the nomenclature and conventions presented to you in class. Keep the table with you like the periodic table of elements in chemistry, you will refer to this AA table throughout the course. The three letters in parentheses are the 3-letter shorthand, and the letter in the red circle is the 1-letter shorthand: e.g., arginine, Arg, R. To read Figure 1, the AA in the top left is arginine. Note that selenocysteine (Sec, U) is not a common amino acid and can be skipped. A table of the common amino acids is provided in Figure 1. Use flash cards, whiteboards, or any other method of repetitive memorization. To learn the structures, names, and shorthand, the best method here is memorization. That is a daunting task for 20 amino acids. Most biochemistry courses will require you to know the following: the amino acid name, the structure, the pKa of ionizable hydrogens, and both the 3-letter and 1-letter shorthand. Always keep in mind, structure gives function. Errors in amino acid placement do occur and can lead to cell death in some instances. The AAs are strung together by ribosomes that read the instructions given to it by the mRNA. These proteins are made up of smaller building blocks called amino acids (AA). Proteins are complex biomolecules that perform critical roles in the cell.

When genes are expressed, the DNA is transcribed into mRNA that is then translated into proteins.
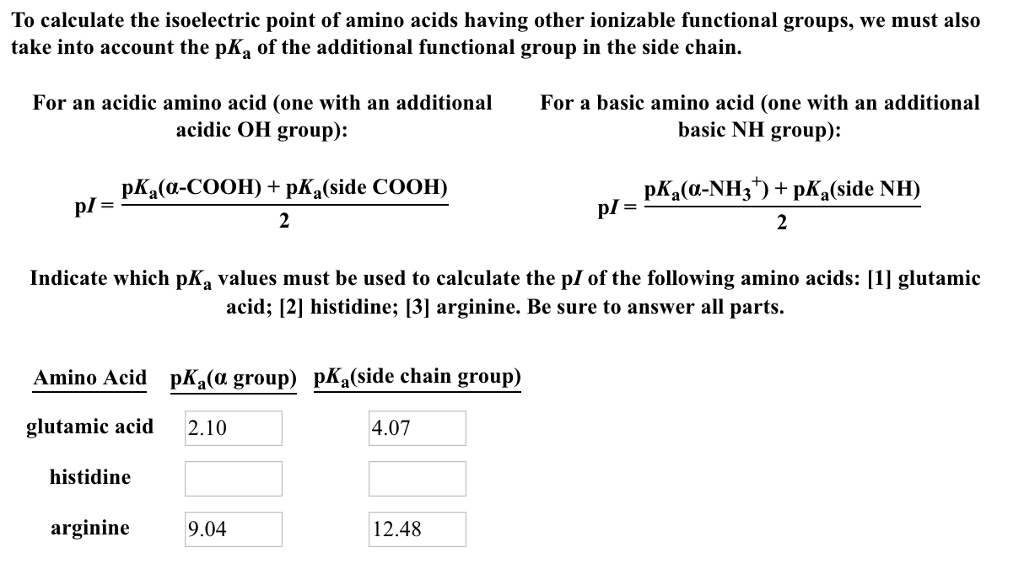
CALCULATE PI OF AMINO ACID WITH R GROUP CODE
The Chemaxon pI values were calculated with the default setting of the plugin.In biochemistry, DNA holds the genetic code for life. Here is a table with the predicted and experimental pI values for the amino acids. 2 The pH-charge plot for the histidine molecule showing a more complex plot with a pI 8.02. See a more complex pH-charge plot for the histidine molecule as an example.įig. 1 The pH-charge plot of the amino acid valine with a pI value of 6.16.įor molecules that have more ionizable sites the prediction uses the same principles however the pH-charge plot becomes more complex because of the number of microspecies. As the two dissociation constants (the pK a value of the COOH group and the pK b value of the NH 2 group) are far away from each other, we get a very simple pH-charge plot.įig. So there are only 2 microspecies (1 with +1 and 1 with -1 charge ) with exactly opposite charges.

The following examples were calculated with the default settings of the Isoelectric Point Plugin.įor amino acids that have just 2 ionizable sites it is easy to predict the pI as there are only 3 microspecies, and 1 of them has 0 net charge.

The accuracy of the prediction is heavily dependent on the accuracy of the pK a prediction and the pH step size. Predicting the isoelectric point for molecules with many ionizable sites is not easy in general as there are many microspecies. The pH step-size can be set for the algorithm. Our pI prediction algorithm approaches the (unique) zero point of the total charge function (which is a function of the pH). The isoelectric point is the pH where this sum is 0, that is The total charge can be expressed by the weighted sum of the net charges of the microspecies (let the charge of the i th microspecies be C i ), using the distributions as weights (let the distribution of the i th microspecies be d i ): (A molecule with N ionizable sites have 2 N -1 microspecies we do not count the natural form here as a microspecies) At a given pH the molecule is present as a set of microspecies with a given distribution, where each microcpecies has a net charge. Molecules with ionizable sites have many microspecies in aqueous solution. the solubility of a molecule at a given pH predicting the pI for proteins can help in their separation and purification processes. Knowing the pI can be important for predicting e.g. The isoelectric point (pI) of a molecule is the pH at which the molecule carries no net charge. This background material discusses the theory behind our isoelectric point calculation:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
